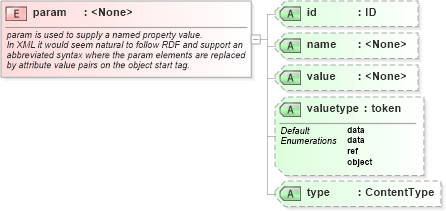
<xs:element name="param">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
param is used to supply a named property value.
In XML it would seem natural to follow RDF and support an
abbreviated syntax where the param elements are replaced
by attribute value pairs on the object start tag.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:ID" />
<xs:attribute name="name" />
<xs:attribute name="value" />
<xs:attribute name="valuetype" default="data">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:token">
<xs:enumeration value="data" />
<xs:enumeration value="ref" />
<xs:enumeration value="object" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="type" type="ContentType" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
|