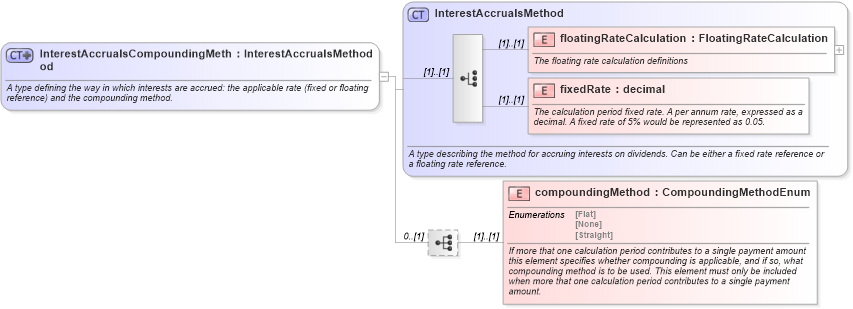
<xsd:complexType name="InterestAccrualsCompoundingMethod">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation xml:lang="en">A type defining the way in which interests are accrued: the applicable rate (fixed or floating reference) and the compounding method.</xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:complexContent>
<xsd:extension base="InterestAccrualsMethod">
<xsd:sequence minOccurs="0">
<xsd:element name="compoundingMethod" type="CompoundingMethodEnum">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation xml:lang="en">If more that one calculation period contributes to a single payment amount this element specifies whether compounding is applicable, and if so, what compounding method is to be used. This element must only be included when more that one calculation period contributes to a single payment amount.</xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:element>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:extension>
</xsd:complexContent>
</xsd:complexType>
|