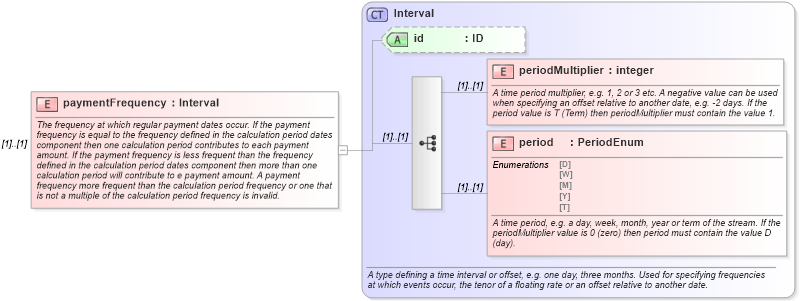
<xsd:element name="paymentFrequency" type="Interval">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation xml:lang="en">The frequency at which regular payment dates occur. If the payment frequency is equal to the frequency defined in the calculation period dates component then one calculation period contributes to each payment amount. If the payment frequency is less frequent than the frequency defined in the calculation period dates component then more than one calculation period will contribute to e payment amount. A payment frequency more frequent than the calculation period frequency or one that is not a multiple of the calculation period frequency is invalid.</xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:element>
|